IOT and the fundamental transformation in industrial production
Author:
Mohsen Shamsi
Category:
Articles
Study time: 8 minutes
Internet of Things and the fundamental transformation in industrial production: from traditional industry to smart factories of the future
Global industry is on the verge of a major transformation, a transformation known as Industry 4.0. In this industrial revolution, technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced robotics, 3D printing, and big data play a central role. Among these technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) has a special place as the link between machines, people, software, and data.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) not only helps improve productivity and reduce costs, but also allows industries to operate more flexibly, data-driven, and intelligently. This article takes an in-depth look at the concept of IoT in industries, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future.
What is IoT in industry?
The Internet of Things in industry means connecting equipment, machinery, sensors and various devices to a smart network that enables real-time data exchange. Data collected through sensors can include things like temperature, humidity, pressure, vibration, energy consumption, production speed and even environmental conditions. This information is processed and analyzed with the help of cloud platforms and artificial intelligence algorithms and then used to optimize processes.
Simply put, IoT is the brain and nervous system of the factories of the future, enabling them to “see, hear, analyze and react quickly.”
Key applications of the Internet of Things in industrial production
۱٫ Real-time monitoring of equipment
One of the first and most important applications of IoT in industry is real-time monitoring of equipment performance. Sensors continuously record data such as temperature, pressure, vibration levels and energy consumption and send it to a central dashboard. This capability allows managers and operators to monitor the status of the production line at any time.
Benefits:
Rapid identification of potential problems before they become a crisis
Prevent sudden production line stops
Increase transparency in processes
۲٫ Predictive Maintenance
In traditional industries, maintenance was done reactively (after a failure) or periodically, which was both costly and caused unnecessary downtime. IoT enables predictive maintenance by analyzing sensor data.
Example: If an unusual vibration is registered in a motor, the system warns that its bearings probably need to be replaced. In this way, repairs can be carried out before a complete failure occurs.
Benefits:
Reduces emergency repair costs
Increases equipment life
Reduces unexpected downtime
۳٫ Intelligent coordination of machinery
IoT-connected machines can communicate intelligently with each other. For example, if machine A slows down production, machine B will automatically coordinate to avoid bottlenecks.
The result: increased productivity across the entire system and smoother production flow.
۴٫ Energy consumption optimization
Energy is one of the most important costs for industries. IoT identifies inefficient patterns by monitoring the consumption of electricity, water, gas and other energy sources in real time. Analytical algorithms then provide suggestions for reducing consumption.
Examples:
Automatically turning off unused devices
Intelligent adjustment of cooling and heating systems
Identifying and upgrading high-energy machinery
۵٫ Real-time quality control
In many production lines, quality control is performed manually after production is finished. IoT is revolutionizing this process and enabling real-time quality control.
Methods:
Using smart cameras and machine vision algorithms to identify defects
Precisely measure physical properties of products with advanced sensors
Real-time data analysis to quickly correct the production process
Benefits:
Reduce waste
Increase production accuracy
Improve customer satisfaction
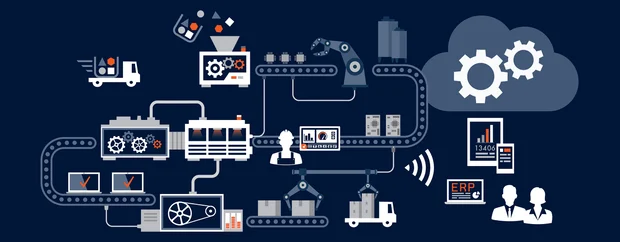
۶٫ Smart supply chain management
IoT is not just used in factories; it plays an important role in the entire supply chain. By installing GPS and RFID sensors, it is possible to accurately track raw materials and finished products.
Applications:
Tracking the status of shipments during transportation
Intelligent inventory management
Predicting future needs by analyzing market and production data

Key Technologies in Industrial IoT
۱٫ Industrial communication protocols
Protocols such as MQTT, OPC UA, and Modbus allow machines to transfer data securely and quickly.
۲٫ Cloud Computing
Industrial big data is stored and processed in cloud platforms. This infrastructure enables data analysis on a large scale.
۳٫ Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI analyzes data collected from IoT and identifies hidden patterns. These patterns are used for automated or semi-automated decision making.
۴٫ Digital Twin
A digital twin is a virtual version of equipment or a production line that is created using IoT data. This virtual model helps managers simulate, predict, and optimize processes.
۵٫ ۵G networks
This high-speed, ultra-low-latency technology enables simultaneous communication between thousands of industrial devices and will be the backbone of future smart factories.
Benefits of implementing IoT in industries
- Increase productivity through machine coordination and data analysis
- Reduce costs with energy efficiency and predictive maintenance
- Improve product quality with real-time control
- Enhance employee safety by monitoring hazardous environmental conditions
- High flexibility in response to market changes and customer demand
- Reduce waste and produce more sustainably in line with environmental responsibilities
Challenges of implementing IoT in industries
Although IoT has many benefits, industries face challenges in its implementation:
- Cybersecurity: The widespread connectivity of devices to the internet increases the risk of cyberattacks and intrusions.
- Initial costs: Investments in sensors, software, and infrastructure are heavy.
- Systems integration: Integrating new technologies with legacy equipment can be difficult.
- Expertise required: Data analysis and management of IoT systems require specialized human resources.
- Scalability: Deploying IoT systems on a large scale requires advanced infrastructure.
The future of industrial production with the Internet of Things (IIOT)
There are several major trends and developments that can be predicted for the future of industrial manufacturing with the Internet of Things (IoT). These developments will go beyond the simple use of sensors and monitoring and move towards fully intelligent factories.
۱٫ Autonomous Factories
In the future, IoT, along with artificial intelligence and robotics, will create factories that can manage the production process without human intervention. Devices will communicate with each other, identify problems, and even find solutions automatically.
Example: Imagine a production line where if a robot malfunctions, the IoT system automatically transfers the work to another robot, registers the order for spare parts, and coordinates the repair schedule.
۲٫ Mass Customization
With the help of IoT and accurate data on customer needs, industries will be able to produce in a flexible and personalized way. That is, products can be produced based on customer taste or order, even in high volumes.
۳٫ Combining IoT with new technologies
Blockchain: For greater transparency in the supply chain and fraud prevention.
3D Printing: For rapid production and customization of parts based on IoT data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): For forecasting market demand and automatically optimizing processes.
5G and 6G: For real-time communication of thousands of devices without latency.
۴٫ Sustainability and green production
IoT helps industries optimize energy and resource consumption. The future of industrial production is moving towards green factories, where waste and emissions are minimized. Companies that use IoT for sustainability will both reduce costs and fulfill their social responsibility.
۵٫ Hybrid Workforce
In the future, the role of humans in factories will change. Workers will delegate repetitive tasks to robots and intelligent systems, and they will focus more on data analysis, monitoring, and strategic decision-making. This means a combination of humans + machines.
۶٫ Data-Driven Manufacturing
Data will become the most important asset in industries. Factories of the future will make decisions based on advanced data analytics:
When to increase or decrease production?
Which product is most profitable?
When does the production line need to be changed?
۷٫ Resilience to crises
Experiences like the coronavirus pandemic have shown that industries need to be more flexible. IoT will help factories in the future react more quickly to market changes, supply chain crises, or even labor shortages.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things is a key pillar of the transformation of industrial manufacturing. From real-time monitoring of equipment to intelligent quality control, from energy management to a more transparent supply chain, IoT has transformed everything.
Despite challenges such as cybersecurity and upfront costs, industries have no choice but to move towards smart, data-driven factories. The competitive future of the market will only fall into the hands of those who take steps towards IoT implementation today.
The key question is: Is your industry ready to enter the era of IoT and take advantage of its unparalleled opportunities?
Dinasoft's software


Free consultation
If you need advice in the field of software, you can contact us. Just call us. . .
Tehranpars first square, Maleki St., 46, Unit 4
Notification
By entering your email in this section, you will find out about the latest articles published on the site